When it comes to scientific computers, speed, accuracy, and usability are very important. You need tools that you can rely on and that work well, whether you're working with differential equations, signal processing, or statistical data. SciPy is a strong, open-source tool designed for scientific and technical computing. It makes Python even more powerful. Scientists and engineers already like Python because it is easy to use.
SciPy extends the capabilities of the core Python language by providing a wide range of modules designed specifically for scientific tasks. From mathematical constants to advanced linear algebra, SciPy serves as a one-stop solution for complex computational needs. This post will walk you through everything you need to understand about the SciPy library — what it is, where it's used, how it stands out, how to install it, and its core functionalities.
What is SciPy?
SciPy (pronounced “Sigh Pie”) stands for Scientific Python. It’s an open-source Python library built on top of NumPy and is used primarily for scientific and engineering applications. While NumPy offers core functionalities for array manipulation and basic numerical operations, SciPy expands on that foundation by incorporating advanced algorithms for optimization, integration, interpolation, signal processing, and more. In essence, SciPy serves as a toolbox filled with specialized functions for professionals working in data science, physics, engineering, and mathematics.
Where is SciPy Used?

SciPy finds application across a wide range of scientific and engineering domains. Here are a few fields where it shines:
- Data Analysis: Through modules like scipy.stats, SciPy supports advanced statistical functions for hypothesis testing, probability distributions, and descriptive analytics.
- Engineering: Used for signal processing, system simulation, and solving differential equations that appear frequently in engineering models.
- Physics and Astronomy: Enables modeling of physical systems, solving complex equations, and conducting simulations in areas like quantum mechanics and celestial mechanics.
- Finance: From modeling financial systems to portfolio optimization, SciPy is used to perform time series analysis and risk evaluation.
- Machine Learning: While specialized libraries like scikit-learn exist, SciPy provides essential components such as optimization, interpolation, and statistical analysis for machine learning pipelines.
How is SciPy Different from Other Libraries?
Several Python libraries are built for scientific tasks, so what makes SciPy special?
- Built on NumPy: SciPy is an extension of NumPy, providing additional functionality on top of NumPy’s arrays and matrix operations.
- Comprehensive Toolkit: Unlike Pandas (which focuses on data manipulation) or Matplotlib (for visualization), SciPy covers multiple areas of scientific computation, making it a more versatile library.
- Modular Structure: SciPy is organized into different sub-packages (or modules), each targeting a specific scientific need.
- Integration Friendly: It works smoothly with other scientific libraries like Matplotlib, SymPy, and Pandas, making it easy to create full-fledged data processing workflows.
Installing SciPy
Installing SciPy is a straightforward process, especially if you already have Python and pip installed.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure that:
- You have Python 3.7 or higher installed.
- You have pip, Python’s package manager, ready to use.
You can check this using:
python --version
pip --version
Installation Command
To install SciPy, use:
pip install scipy
Once installed, verify it by launching a Python shell and running:
import scipy
print(scipy.__version__)
If no errors appear and the version is displayed, you’re ready to start exploring SciPy’s capabilities.
Core Modules of SciPy
SciPy is broken down into several key modules, each designed to tackle specific types of scientific problems. Let’s explore the most widely used ones:
scipy.stats – Statistics
This module supports a wide range of probability distributions, statistical tests (t-tests, chi-square), and descriptive statistics (mean, variance, skewness). It’s ideal for hypothesis testing and probabilistic modeling.
scipy.linalg – Linear Algebra
Provides all the tools for working with matrices: matrix factorizations (LU, QR, SVD), solving linear systems, and calculating determinants. It’s an advanced counterpart to NumPy’s basic linear algebra functions.
scipy.fft – Fourier Transforms
For signal processing, this module enables fast computation of Fourier transforms and inverse transforms in one or more dimensions. It supports both real and complex data.
scipy.optimize – Optimization
This module is used to find minima and maxima of functions, as well as root-finding for equations. It is widely used in machine learning, economics, and engineering optimization.
scipy.interpolate – Interpolation
Enables the estimation of unknown values between known data points. Useful in curve fitting, data smoothing, and upsampling tasks.
scipy.integrate – Integration and Differential Equations
Offers numerical integration tools such as the trapezoidal rule and Simpson’s rule, along with solvers for ordinary differential equations (ODEs).
scipy.signal – Signal Processing
Includes functionality for filtering, convolution, and spectral analysis. Often used in audio and electronics applications.
scipy.spatial – Spatial Data and Geometry
Supports distance calculations, spatial indexing (e.g., KDTree), and geometric algorithms like Delaunay triangulation and convex hull computation.
scipy.io – File Input/Output
Handles reading and writing data in various formats, including MATLAB .mat files, WAV audio files, and NumPy binary formats.
scipy.ndimage – Image Processing
Designed for multi-dimensional image analysis. Includes functions for filters, morphology operations, and measurements on binary and grayscale images.
scipy.constants – Physical Constants
Gives access to commonly used scientific constants such as the speed of light, Planck’s constant, and gravitational constant, as well as unit conversions.
scipy.sparse – Sparse Matrices
Ideal for handling large, memory-efficient matrices that contain mostly zeros. Supports efficient matrix multiplication, storage, and decomposition.
scipy.cluster – Clustering
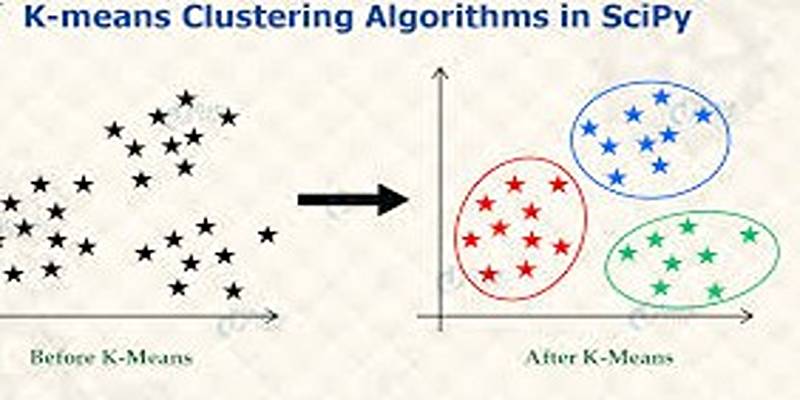
Provides algorithms for data clustering, including hierarchical clustering and k-means, which are fundamental in unsupervised machine learning and data exploration.
Conclusion
SciPy is more than just a library—it’s an essential toolkit for anyone working in science, engineering, data analysis, or machine learning. By building on the foundation of NumPy and offering a comprehensive suite of specialized modules, SciPy has established itself as a powerhouse in the scientific Python ecosystem. Whether you're a beginner looking to solve simple equations or a researcher handling complex models, SciPy provides the tools you need to bring your ideas to life, all while saving time and effort.